Spinal backfill
Neurons that project to the spinal cord, color-coded by depth.

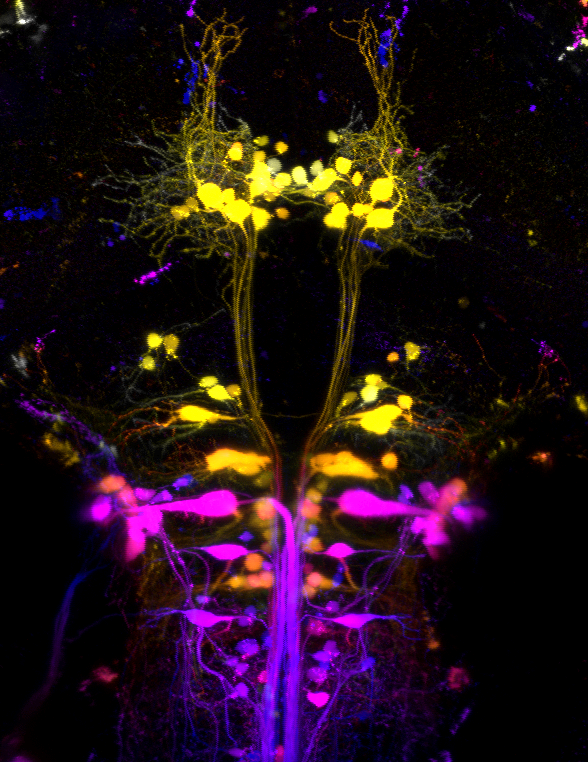
The vestibular nucleus neurons and their projections
A fluorescent image from a transgenic line of zebrafish (pSam-gal4;UAS-Brainbow-V) that labels a subset of individual neurons in the hindbrain and their projections. Neurons are visible as small spots of different color, with matching thin lines corresponding to their projections.
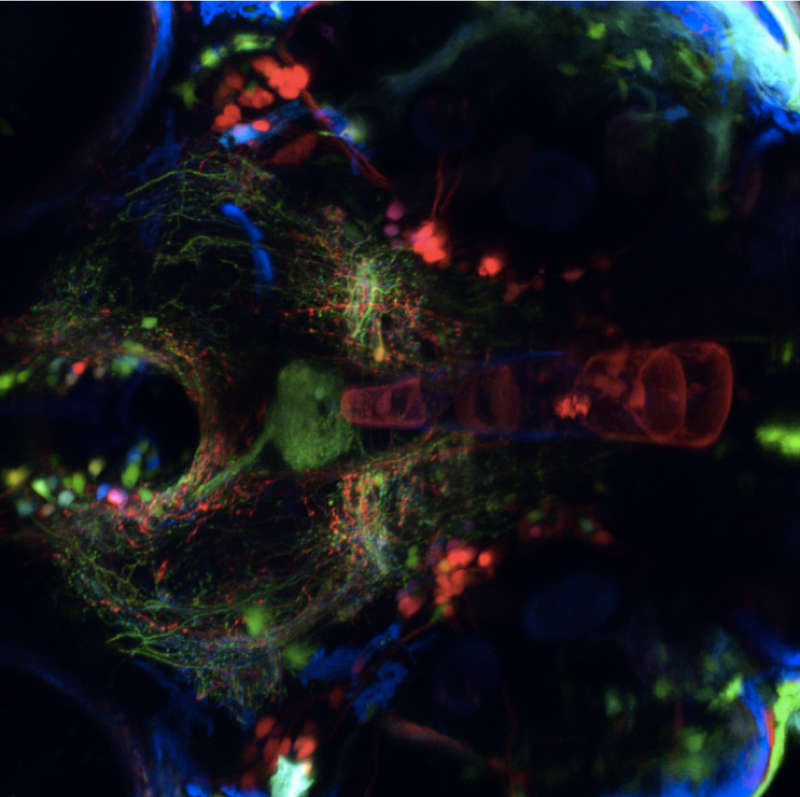
The stato-acoustic ganglion
A fluorescent image from a transgenic line of zebrafish (pSam-gal4;UAS-Brainbow-V) that labels a subset of individual neurons at the level of the stato-acoustic and trigeminal ganglia. Neurons are visible as small spots of different color, with matching thin lines corresponding to their projections.
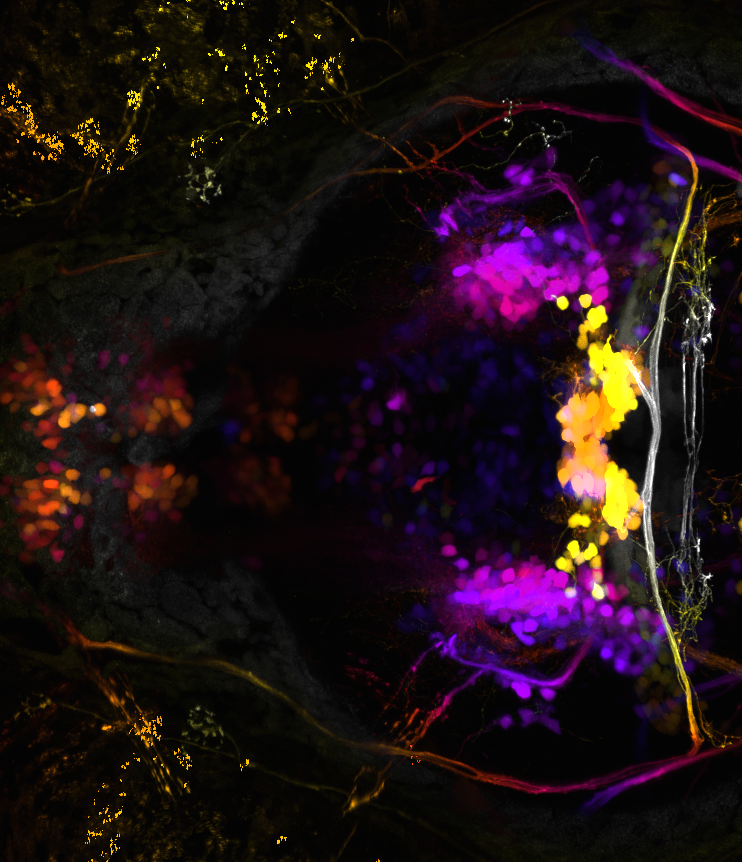
Cranial motor neurons
A fluorescent image from a transgenic line of zebrafish (islet-GFP) that labels the cranial motoneurons. Depth is color-coded, with white/yellow being closest to the top of the fish. The oculomotor and trochlear nuclei that control torsional eye movements are visible as clusters of yellow neurons. Their associated axons that comprise the cranial nerves can be traced all the way to the eyes in the upper and lower-left corners of the image.

Utricular hair cells and afferents
An image taken from the inner ear of a double transgenic fish, with the hair cells labelled in green and the afferent neurons in the stato-acoustic ganglion labelled in red.
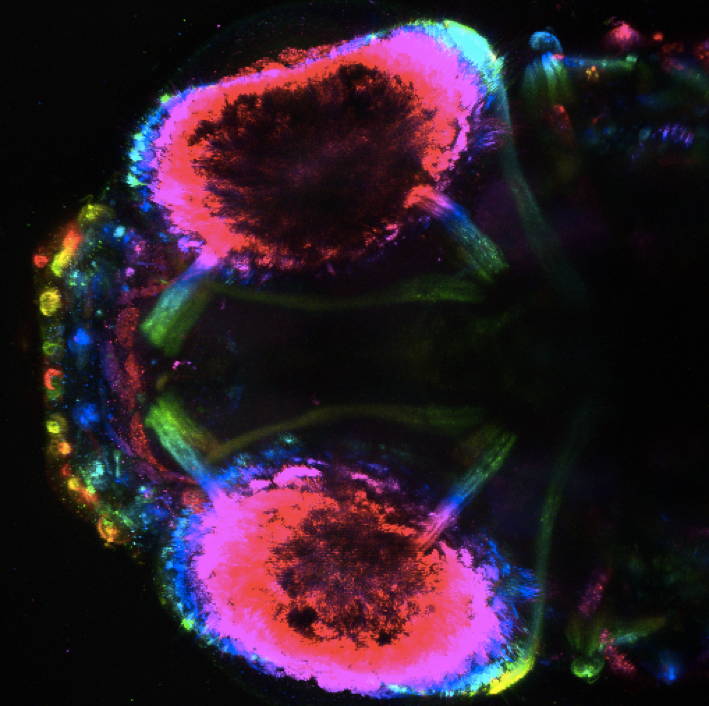
The eyes and associated muscles
A fluorescent image of the head of a transgenic line (unpublished) of zebrafish. Autofluorescence in the eyes is most prominent as two ovals, while six eye muscles (in the same configuration as humans!) can be traced from their attachment points on each eye. The image is color-coded by depth.

Balance apparatus, motor
The motor rotates the platform to generate tilt sensations.
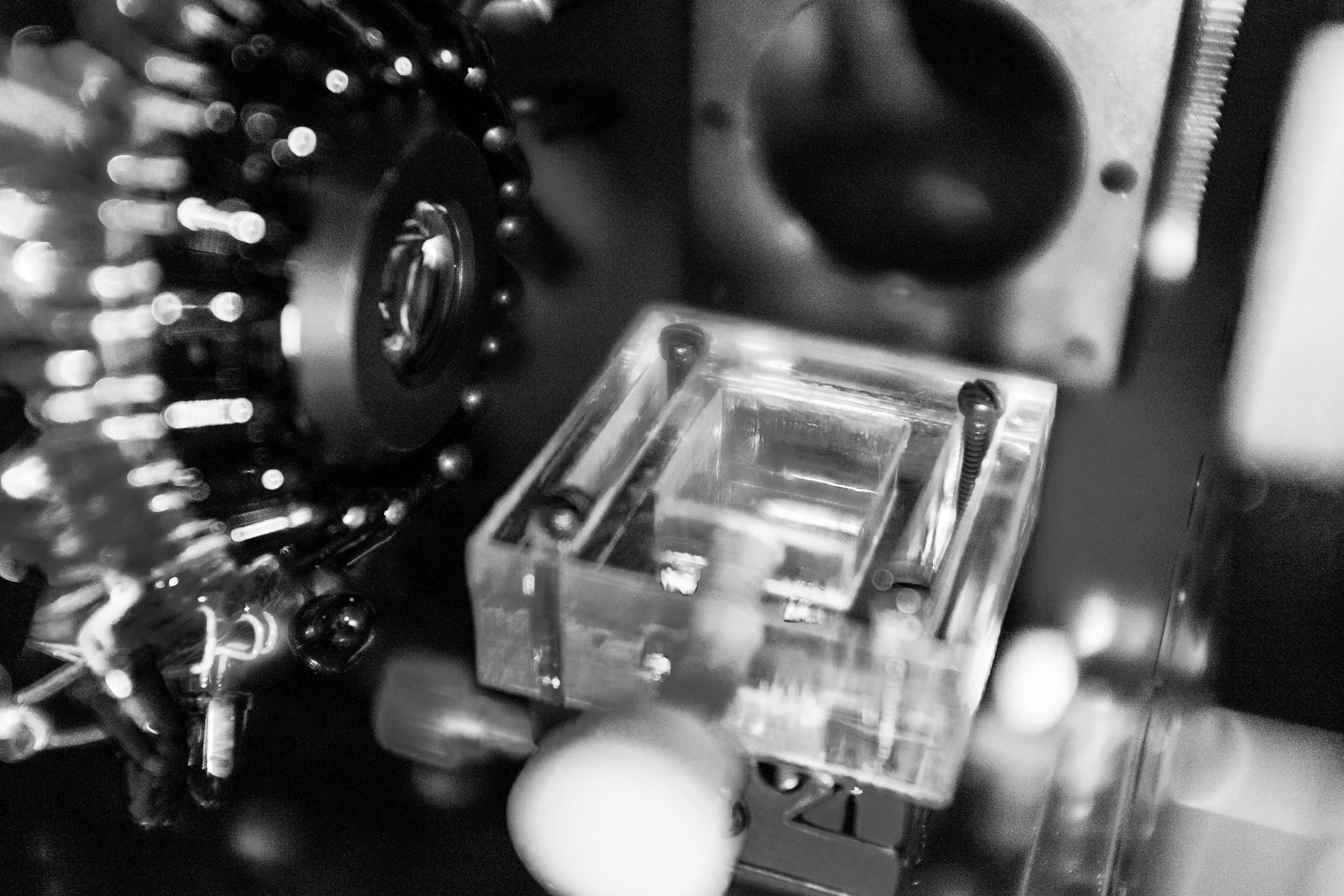
Cuvette holder, objective and IR LED array
Custom-machined transparent acrylic cuvette holder mounted on a goinometer. 5x microscope objective with surrounding LED array visible on the left.
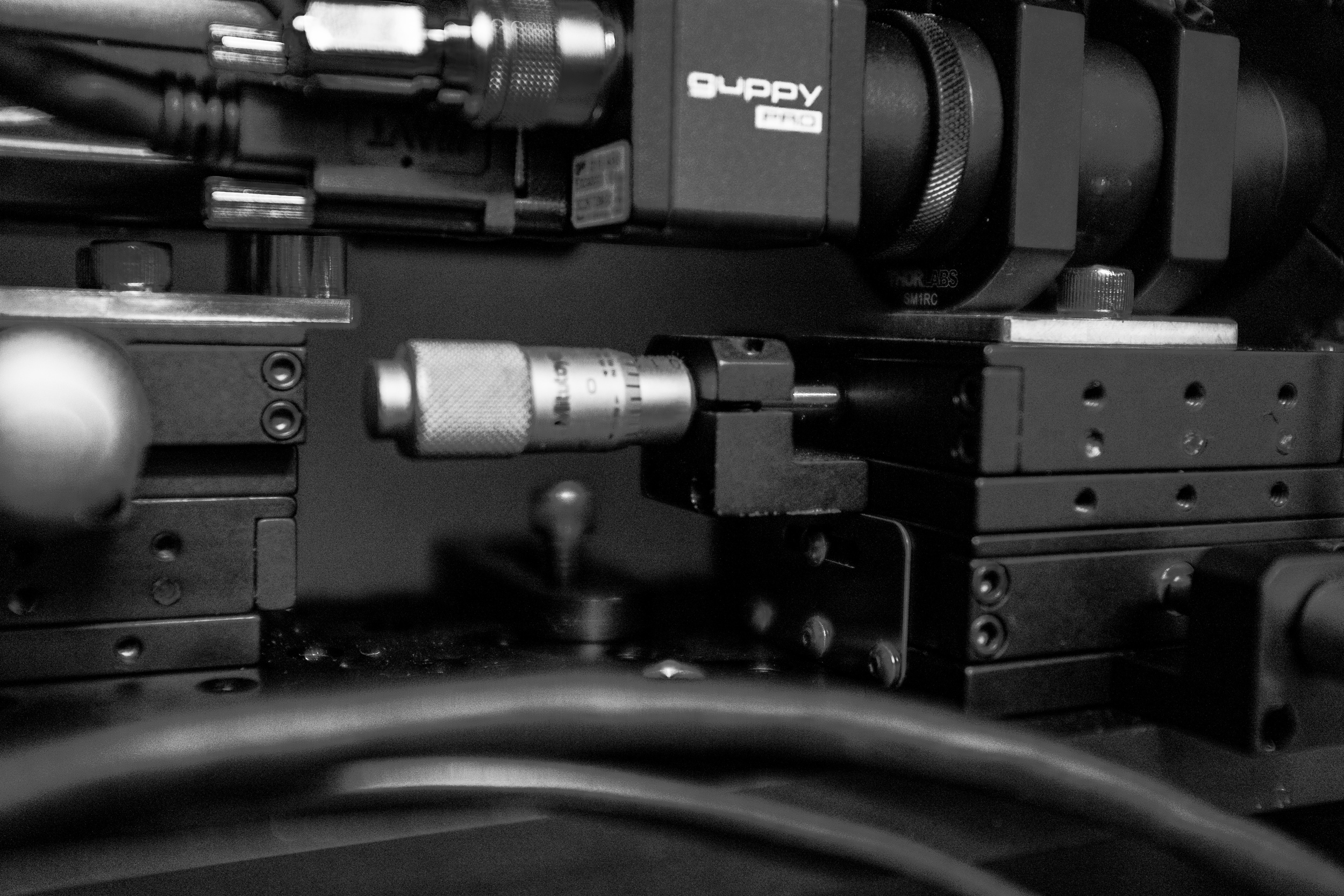

Camera on a 2-axis manipulator
The camera that captures images of the fish eye as it rotates is mounted on a platform that can translate in X and Y to ensure the eye is in focus.
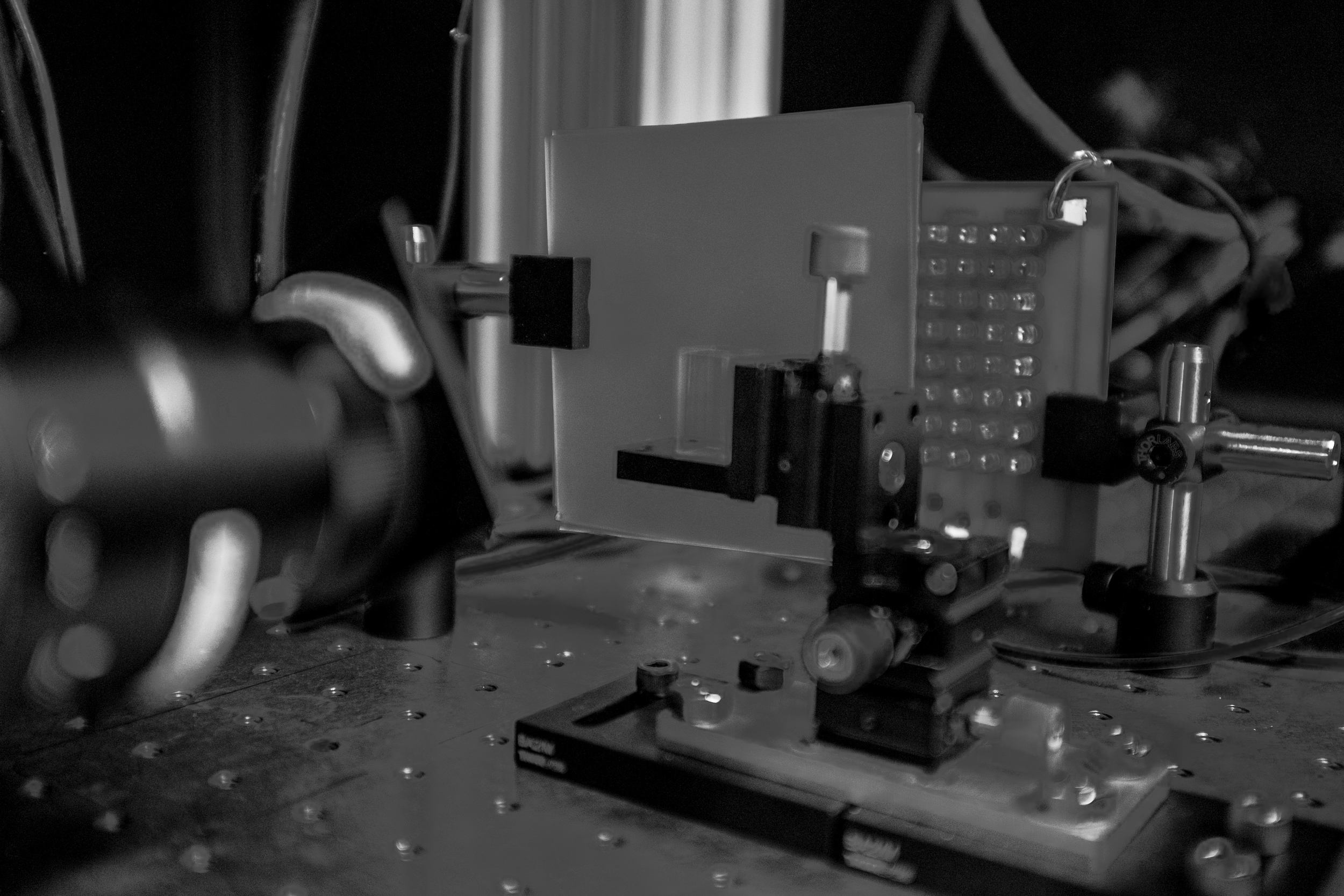
Apparatus for viewing freely moving fish
A simple apparatus for capturing videos of fish moving freely. An LED array sits behind a diffuser screen, while a cuvette (empty of fish) rests on a manipulator to bring it into focus with the camera.
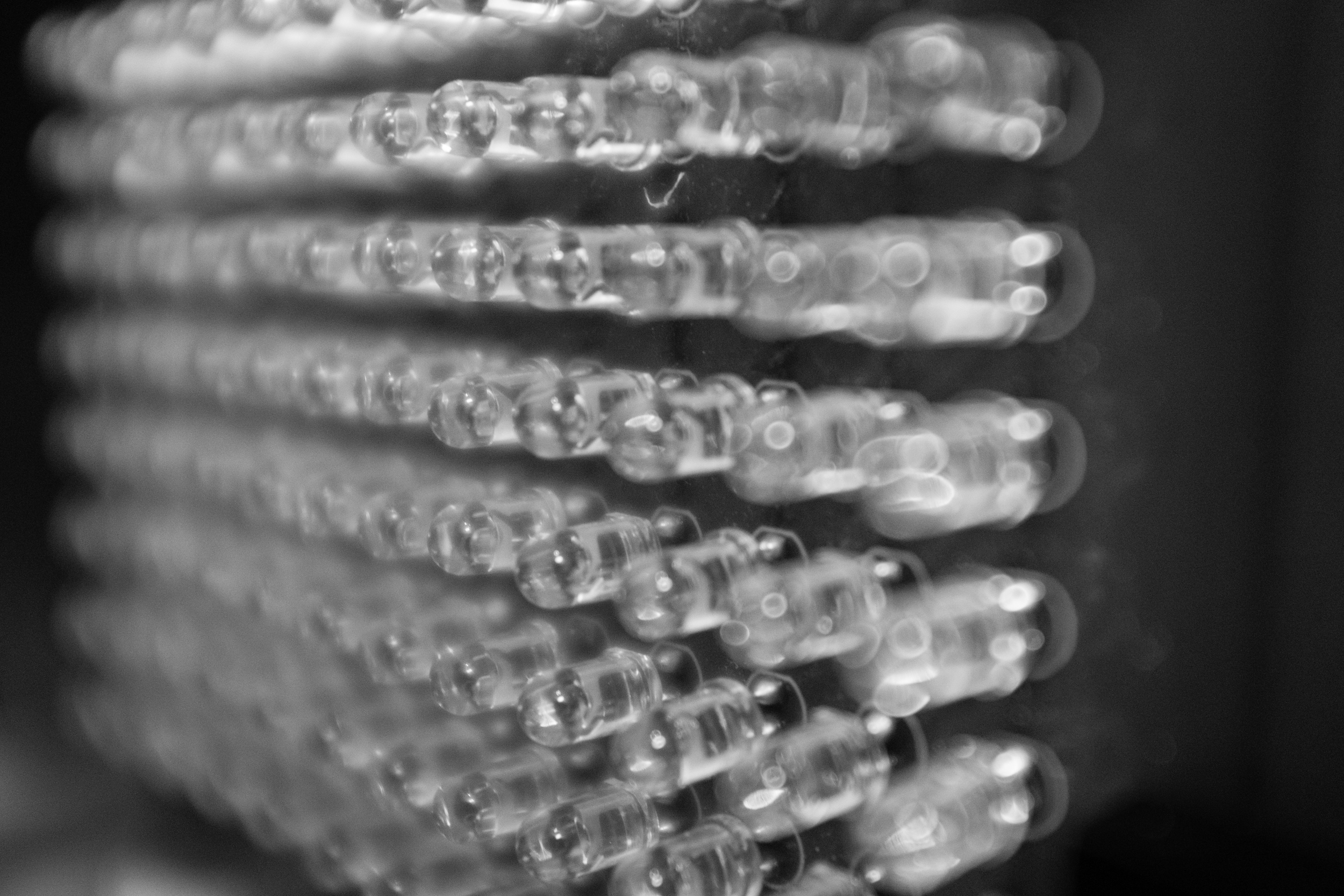

LED array
Custom 8x12 array of 940nm IR LEDs. Handy.

Lasers!
Well, one laser in this image. A fiber coupled, 473nm laser that permits straightforward activation of neurons in fish brains.
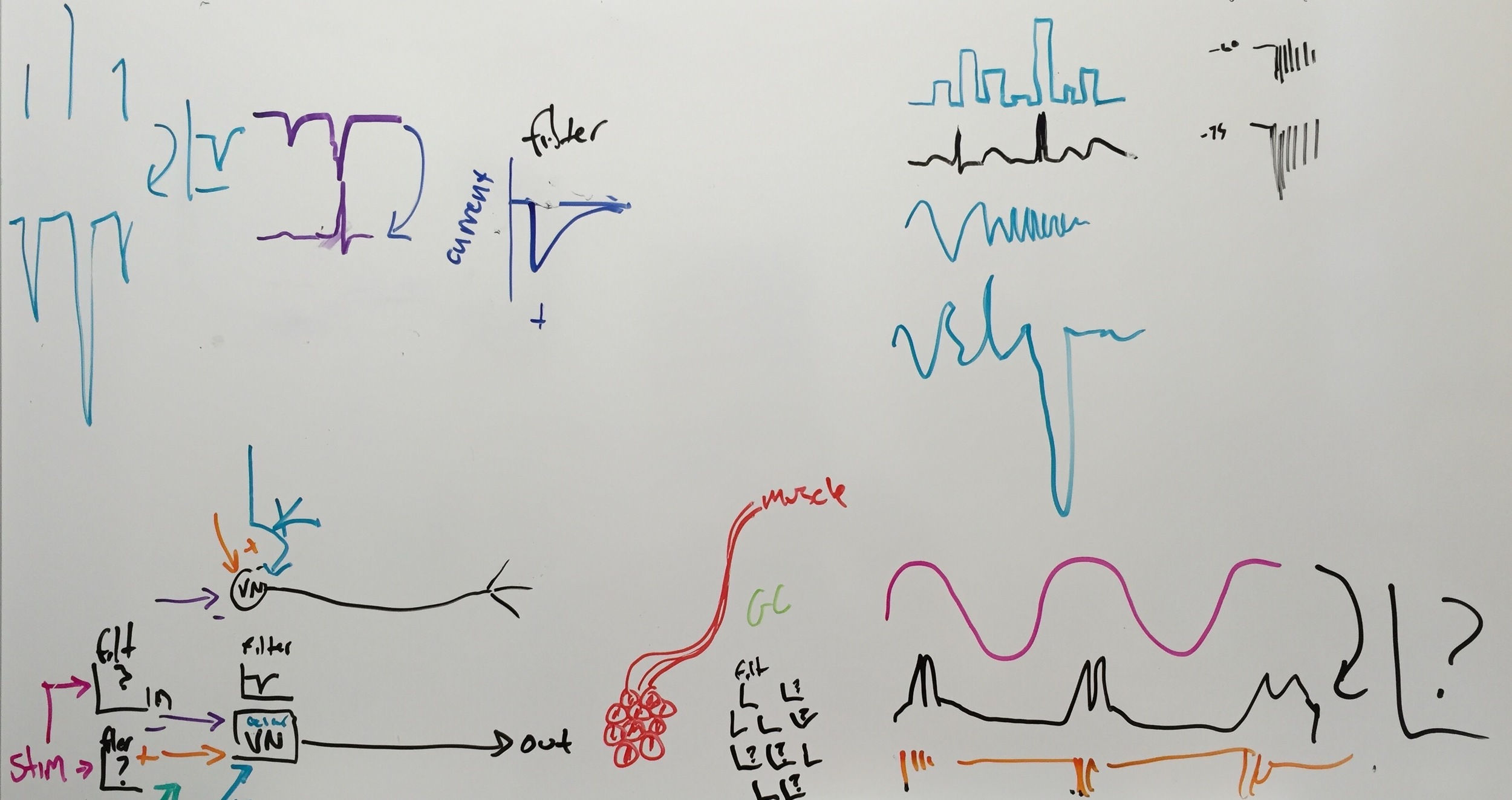
Whiteboard musings, 12/15
Working through the models underlying our work, and the experiments we'll use to test them.












